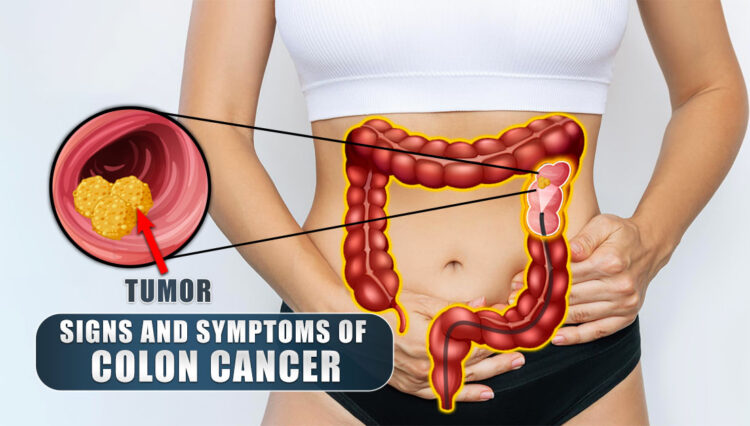
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Colon Cancer
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Introduction
- Colorectal carcinoma/cancer (CRC)
- Cancer involving the large intestine and/or rectum
- Tumor/growth may affect right colon, lest colon, or rectum
- Malignant growth arises from polyp
Epidemiology
- 3rd-4th most common type of cancer
- Approximately 5% of cases are attributed to two genetic causes
- Most common cause of large bowel obstruction in adults
- Mean age of onset is 70 years of age
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Fisk Factors
- Older Age
- >50 years old
- Family history of CRC
- First-degree family members under age of 60
- History of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Dietary History
- Low fiber, processed meats
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Increased BMI
- Genetic conditions
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- Lynch syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Gardner syndrome
- Turcot syndrome
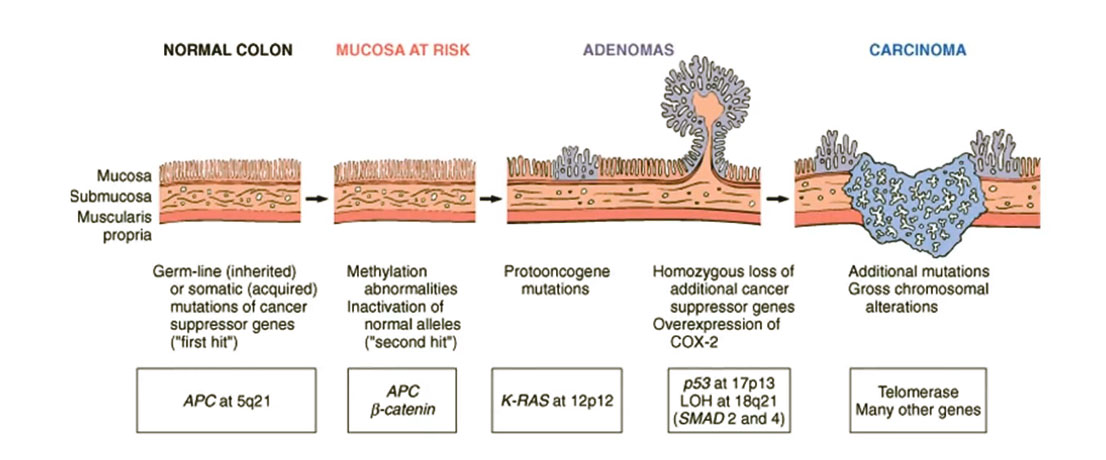
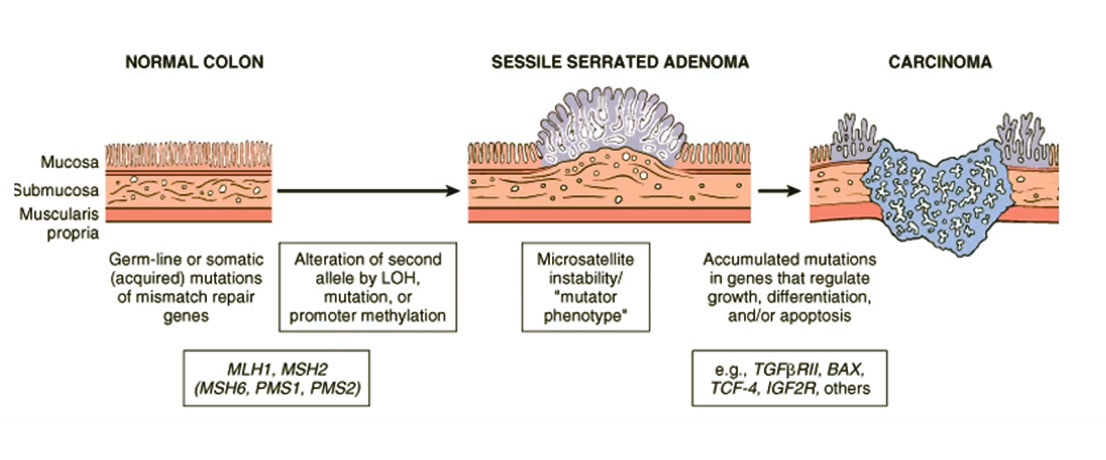
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Pathophysiology
- Colon cancer arises from colonic polyps (adenomas: adenomatous polyps)
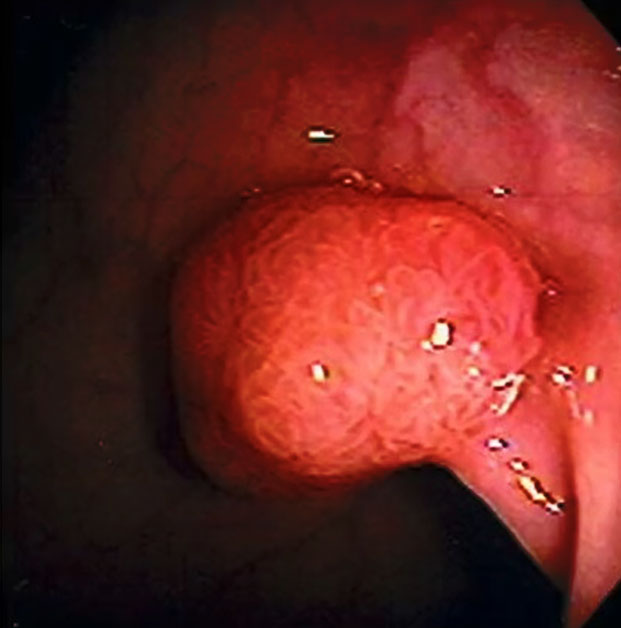
- Adenocarcinomas represent majority of cases
- Endoluminal adenocarcinomas
- 98% are adenocarcinomas
Other tumor types
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
- More likely to occur in HIV-positive/AIDS patients
- Caused by an infection with human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8)
- Carcinoid tumors
- Neuroendocrine tumor
- May excrete vary large amounts of serotonin
- Lymphomas
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Metastasis
Variety of patterns of spread of the cancer
01- Direct invasion/extension
- Grows within bowel, then may spread through bowel wall and invade into other abdominal structures/organs
02- Hematogenous spread
- Via gastrointestinal veins to the portal circulation
- Liver metastases are the most common
- Via lumbar and vertebral arteries
- May affect lungs, brain
03- Lymphatic system
- Regional spread
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Signs & Symptoms
- May be asymptomatic
- Abdominal pain
- Stool changes
- Caliber
- Frequency
- Bowel habit changes
- Alternating constipation and diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Melena and/or hematochezia
- Iron-deficiency anemia
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Other Clinical Features
Signs and symptoms of large bowel obstruction
- Nausea & vomiting
- Constipation
- Obstipation
Rectal Cancer
- Rectal “fullness”, mass
- Tenesmus
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Screening
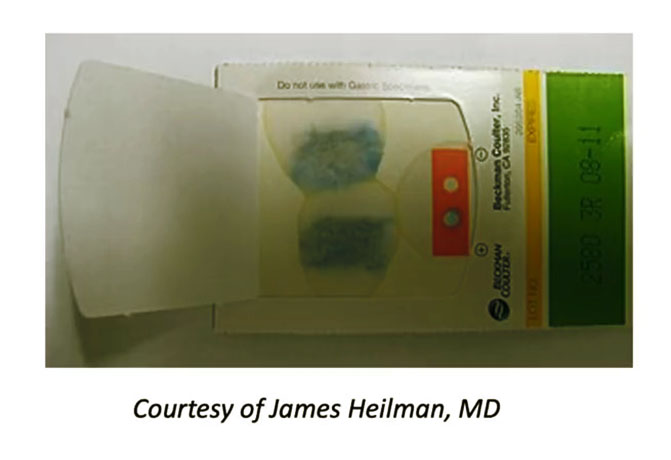
- Fecal occult blood testing (FOBT)
- Also known as stool guaiac test
- Prone to false positives
- Fecal immunochemical test (FIT)
- Preferred over FOBT
- Digital rectal exam (DRE)
Screening should begin at age of 50
Exceptions: Family history of CRC, begin screening at 40; if earlier diagnosis, start screening 10 years before age of onset
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Diagnosis
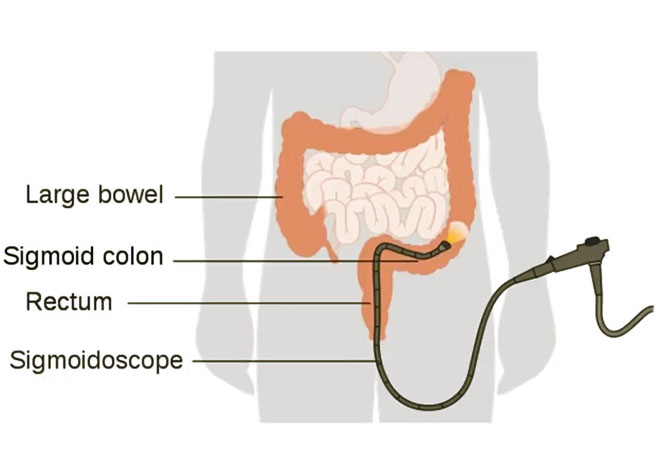
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy
- Can diagnose approximately ¾ of cases
- Requires FOBT/FIT
- Colonoscopy (& Biopsy)
- Most sensitive and specifics
- Every 10 years, unless abnormalities are found
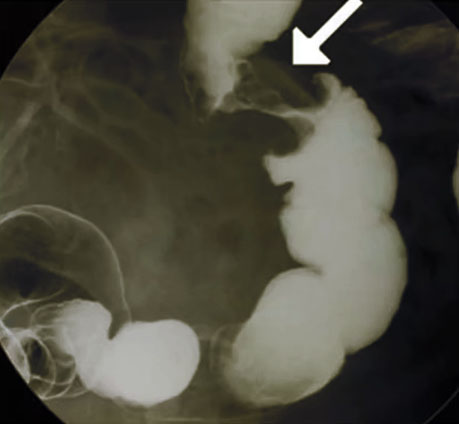
- Barium enema
- “Apple core” lesion
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- Can be used to prognostic purposes (>5 ng/mL)
- Important to measure prior to treatment and during follow-up to assess for recurrence
- CT Scan
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Staging
TNM System of staging (“Tumor, Node, Metastasis”)
Stage 1
T: 1,2 Nodes: 0 Metastasis: 0
Stage 2
T: 3,4 Nodes: 0 Metastasis: 0
Stage 3
T: X Nodes: + Metastasis: 0
Stage 4
T: X Nodes: X Metastasis: 1
T1 – Invasion into submucosa
T2 – Invasion into muscularis propria
T3 – Invasion into muscularis propria and into serosa
T4 – Invasion into adjacent structures or organs
N0 – No regional node involvement
N1 – Metastasis in 1-3 regional nodes
N2 – Metastasis in 4 or regional nodes
M0 – No distant metastases
M0 – Distant metastases
Colon Cancer (CRC) | Treatment & Follow-Up
Non-cancerous polyps
- Polypectomy (colonoscopy)
Surgical resection of cancerous bowel
- Colectomy with primary anastomosis
Rectal Cancers
- Higher recurrence rate
- Resection
Adjuvant therapy in addition to surgery depends on stage of cancer
- Most often for patients with stage 3
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
- Capecitabine with oxaliplatin
- FOLFOX
Palliative if distant spread
For those who have recurrence, 90% will occur within 3 years of surgery
CEA measurement – levels that increase after treatment indicate recurrence